VRI: Increasing Irrigation Efficiency Can Increase Profit Margins
In 2017, the Rainwater Basin Joint Venture (RWBJV) worked with a landowner in Hamilton County to implement Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) on his Wetlands Reserve Easement Program (WREP) enrollment.

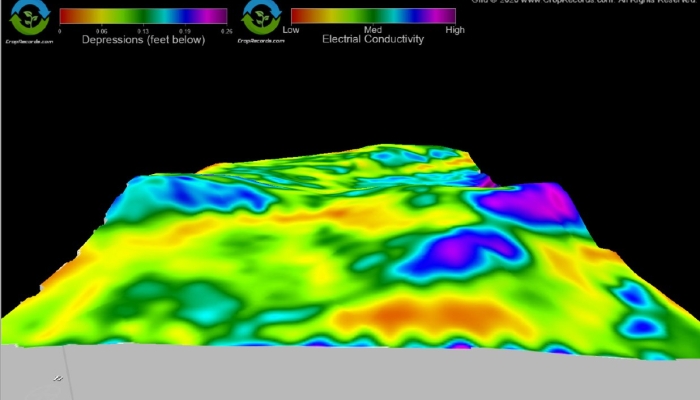
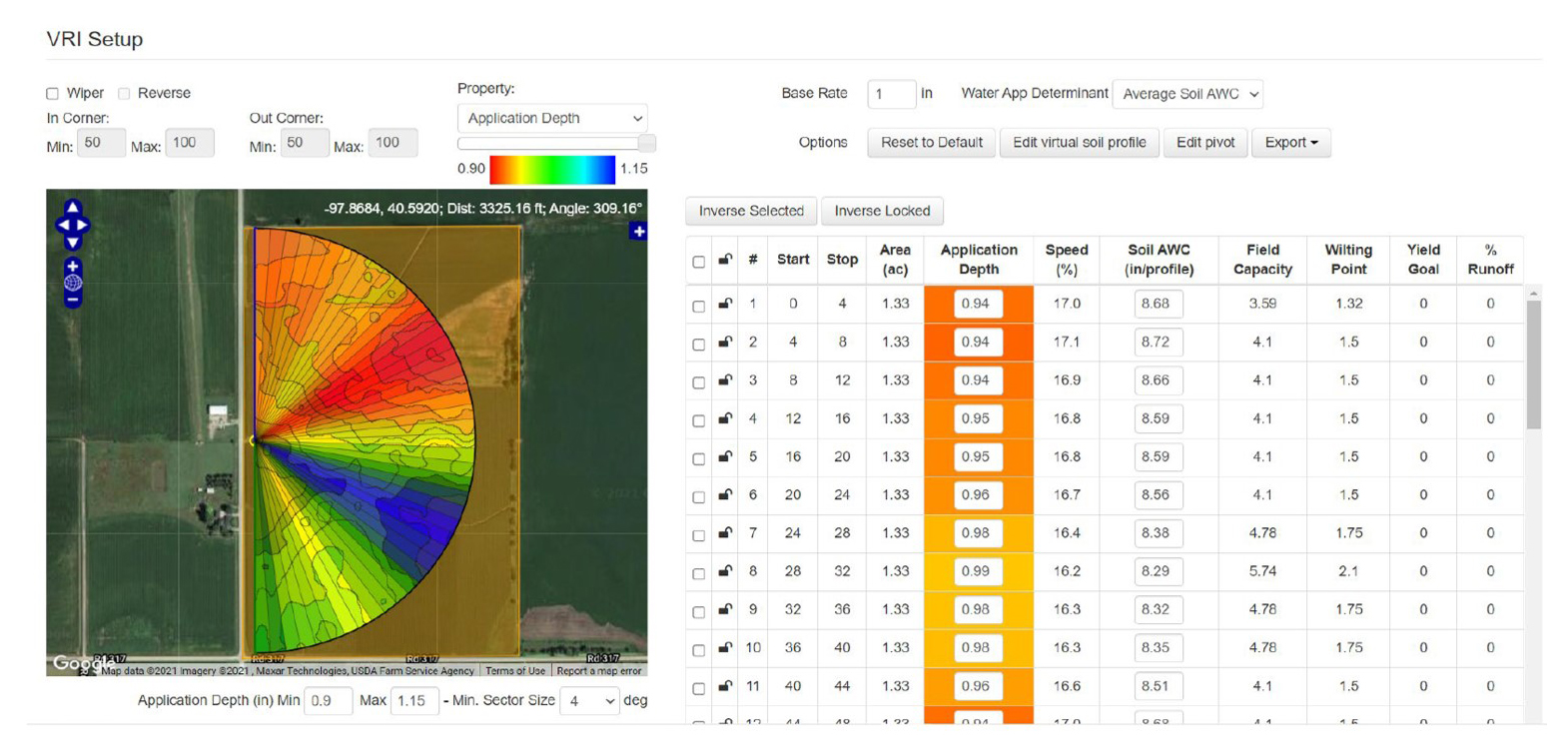
Electroconductivity (EC) mapping was completed on both the cropped area of the property, and the wetland area to assess the soil composition. Soil moisture probes were conducted to report moisture content, soil temperature, and salinity at various depths in the soil profile. A new control panel (including new software) and GPS antenna were added to the center irrigation pivot, as well fitting the pivot with a new sprinkler package. The pivot was now capable of optimizing irrigation application throughout the site. All of the pivot modifications, in combination with the EC mapping/soil moisture probes, allowed for specialists at Precision Agronomy to develop prescriptions for irrigating the crop ground. The RWBJV provided 85% cost-share funding for a 3-year subscription to the prescription irrigation services. Throughout the growing season, landowners receive daily email updates on when and how much to water.
Today, the RWBJV has provided cost-share funding to 11 landowners to implement VRI on their properties. These sites are in four different Natural Resource Districts (Upper Big Blue, Little Blue, Central Platte, and Tri-Basin) in the Rainwater Basin. Recently, data was collected from each of these NRDs/landowners to determine the efficacy of the VRI following the 2022 growing season. For each site, data was provided on the number of acre-inches of water used for irrigation in 2022. Each NRD provided the average water usage (in acre-inches) for producers in their region. This allowed for a comparison between each RWBJV cooperator with VRI water usage versus the average water usage in that NRD.
The irrigation water savings for each of the NRDs was as follows:
-
Upper Big Blue (5 sites): 7.88%
-
Little Blue (3 sites): 24.33%
-
Central Platte (2 sites): 10.35%
-
Tri-Basin (1 site): 48.7%
 The average irrigation water usage across all 4 NRDs in 2022 was 8.68ac-in. The average irrigation water usage of RWBJV cooperators with VRI in 2022 was 7.21ac-in. Thus, the RWBJV cooperators with VRI used 1.48ac-in less to irrigate than other producers in their area in 2022. These cooperating landowners used 16.5% less water than many of their neighbors. It can be assumed that other producers in the NRDs are using VRI as well, so the actual irrigation water savings are likely even higher. In 2022, RWBJV cooperating landowners with VRI on average spent 16.5% less on irrigation than their neighbors.
The average irrigation water usage across all 4 NRDs in 2022 was 8.68ac-in. The average irrigation water usage of RWBJV cooperators with VRI in 2022 was 7.21ac-in. Thus, the RWBJV cooperators with VRI used 1.48ac-in less to irrigate than other producers in their area in 2022. These cooperating landowners used 16.5% less water than many of their neighbors. It can be assumed that other producers in the NRDs are using VRI as well, so the actual irrigation water savings are likely even higher. In 2022, RWBJV cooperating landowners with VRI on average spent 16.5% less on irrigation than their neighbors.
The RWBJV plans to continue monitoring irrigation water use at each of these sites over the next several years to continue assessing how much water, and thereby how much money, producers are saving by implementing VRI technology on their sites and following irrigation prescriptions. Hopefully additional sites will be added to this project as well. It is also important to note that less irrigation water being used on these sites results in more groundwater recharge. So, while individual landowners are benefitting from using less water on their properties, all Nebraskans will benefit from the conservation of limited groundwater resources.